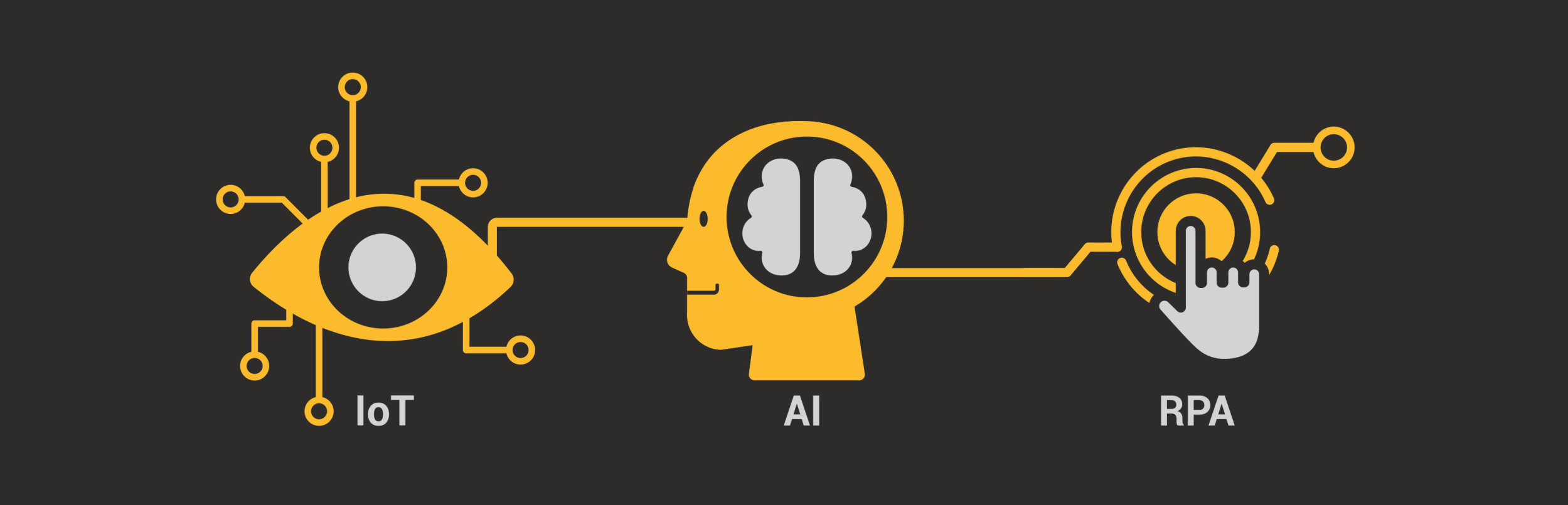
There is a lot of talk about IoT, AI, and RPA revolutionizing supply chains.
What are they? How do they work? What problems do each of them solve in supply chain and logistics? What don’t they solve? And, why is the future of digital supply chains not these technologies in isolation, but a combination of them?
In this article, we will dissect each of these technologies, understand the specific problems that each of them address, and how they can work together to automate the enterprise of the future.
We will begin with an example of one of the best automation systems that the world: humans.
How do these fantastic automation machines called “humans” function?
We use our eyes, ears and other sense to be aware of things around us. We use our minds to analyze and make decisions (almost instantly), and we use our limbs to react – a function that’s driven by the mind – sometimes so quickly that we don’t even know or realize that these three steps are happening in sequence — observation, decision, and action.
One organ or function without the other can greatly cripple our ability to function effectively.
It’s not that different for enterprise operations.
You need to sense what’s happening, you need to analyze and decide instantly about the right course of action, and them act on that decision promptly.
This seamless sequence is what IoT + AI + RPA is capable of achieving, through enterprise automation. With these three technologies working together, an organization can indeed function quite autonomously, like a human-being, making the right decisions promptly, and at scale!
So, how does it work?
Let’s begin by understanding the power of the Internet of Things (IoT), then discuss Artificial Intelligence (AI), further explore the role of Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
IoT – The Internet of Things

The Internet of Things (IoT) is the eyes and ears of your supply chain!
In technical terms, its nothing but real-time data collection and display.
IoT technologies enable the collection of data in an automated or partially automated manner. Solutions like barcodes and hand-held RFID are examples of partial automation in data collection, while solutions like BLE and GSM are examples of fully automated data collection.
See the evolution of supply chain visibility technologies.
The IoT was a big step forward from the ERP era. When the SAPs and the Oracles of the world spoke about digitization in the 1990s and the 2000s, they referred to building a big digital data warehouse on servers or on the cloud.
It’s the advent of IoT though that enables real-time collection and representation.
The power of IoT
1. IoT enables an enterprise to hear from its goods and assets.
2. IoT provides the ability to know in real-time what is happening remotely.
In supply chain terms, this means that you can get to know the location, and sometimes the condition, of your goods in a warehouse or in transit. When it comes to an enterprise assets like equipment or returnable transport items, it means you get to know precisely where they are and what is happening to them without calling someone standing next to them.
So, what is it that IoT is unable to address?
The drawbacks of IoT
The IoT, at its best, is a real-time data machine with some analytics. It doesn’t have a mind of its own. It cannot think.
IoT needs AI if it needs to turn into an intelligent machine – one that can learn from the data it collects, make interpretations, and decide the next course of action, just like humans do.
A good example of this would be a container stuck in a port’s customs area. IoT sensors can tell you in real time where it is, whether it is at a pre-customs spot or post-customs pickup location, and if the door has been opened for inspection.
It cannot, however, tell you what you logically need to do next.
It cannot tell you the likelihood of whether customs will clear the container today, tomorrow, or whether there is something else you need to be wary of, such as an unusual wait time or certain documentation that is needed to have it cleared.
This is where AI comes in!
AI – Artificial Intelligence

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is nothing but “intelligence” exhibited by a non-human entity, such as a system or a tool. Hence, the term “artificial”.
In essence, it is your machine’s mind!
Let’s consider the same example of the container stuck at customs, but now with AI acting based on IoT sensor data.
The AI system would first analyze past patterns and average wait times for the goods at this customs location. It would then use sensor data to relate to the stage of the process it is in. Finally, it would seek more information from non-sensor sources, like the customs portal, before it makes a guesstimate that you could trust.
This is almost similar to how the human mind would work in this situation.
So, why do you need AI when a human can do it?
Because a human cannot do it 10,000 times a day, and with the same efficiency each time, not to mention that he or she will be bored!
Mid and large cap companies handle hundreds or thousands of containers a day, not one.
The power of AI
1. AI has the ability to analyze like a human mind would.
2. AI can predict!
3. AI can prescribe! It can tell you what you should be doing next.
The drawbacks of AI
AI is your system’s brain, but that’s it. AI can decide what is right or wrong, and what you should do, but you need to give it limbs to do something about it. AI without the ability to act out remains “artificial intelligence” not “intelligence action.”
To run a truly automated business using AI, you need real-time action.
This is precisely where RPA comes in!
RPA – Robotic Process Automation
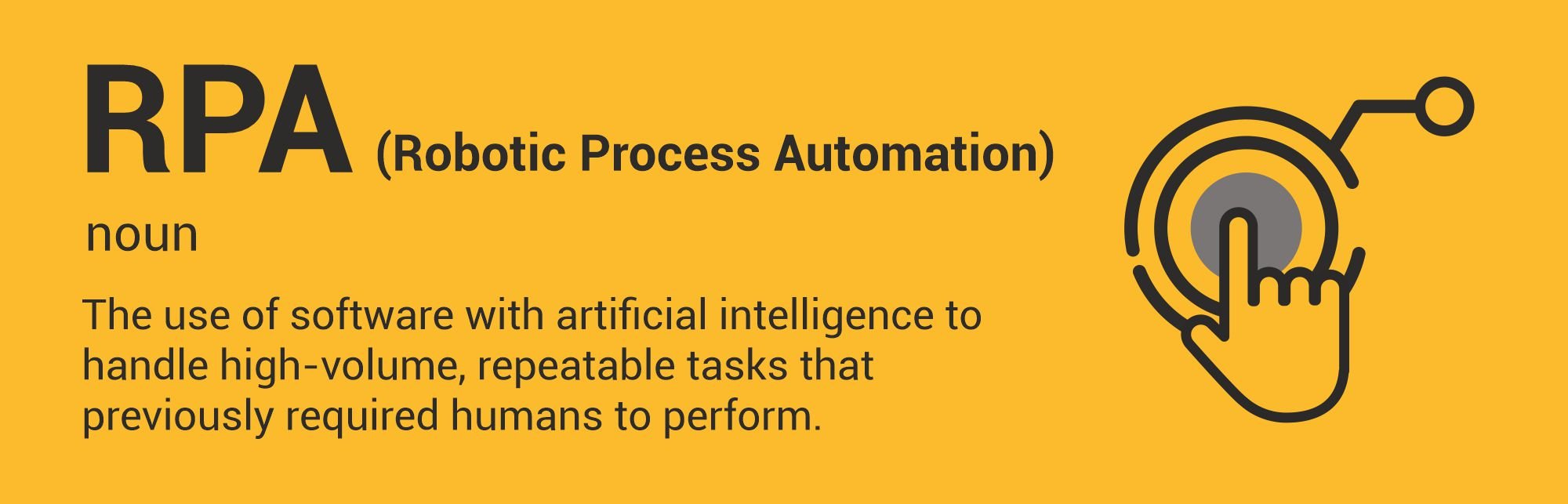
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the ability of a machine or software to perform a pre-programmed task repetitively, but with efficiencies many times higher than a human.
RPA is commonly used in manufacturing and operations processes like invoicing, billing, reporting, and customer service.
The power of RPA
An example of the power of RPA in supply chain would be automated procurements or delivery scheduling. Every time the inventory runs low, the machine re-orders goods from the supplier.
RPA can help with delivery scheduling too. As soon as a product is ready to ship, it can schedule its delivery with a pre-defined vendor by logging into that vendor’s portal and scheduling a pickup using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) bots.
Pretty cool, isn’t it? But, what’s the catch?
The drawback of RPA
The biggest drawback of RPA is that someone or something needs to tell it what to do. RPA cannot make decisions on its own. For example, it cannot decide which supplier is the most cost-effective to re-order from; that intelligence needs to come from a human or AI.
This is where AI comes back into action!
So, AI vs. RPA – What’s the Difference?
AI is the thinker (the mind), while RPA is the actor (the limbs).
AI systems are intelligence-centric while RPA systems are process-centric.
RPA systems are programmed to perform a broad set of actions such as login to a portal and grab a screenshot or key in information. They don’t dwell on what’s a better way to do it, or whether it is worthwhile doing this task in the first place. AI, on the other hand, is more outcome-focussed, correlating data from every source (including what RPA bots can bring) and making the right decision based on time, place, and any other available information.
So, how do they all work together, and where does IoT come into the picture?
An Example of IoT + AI + RPA in Action
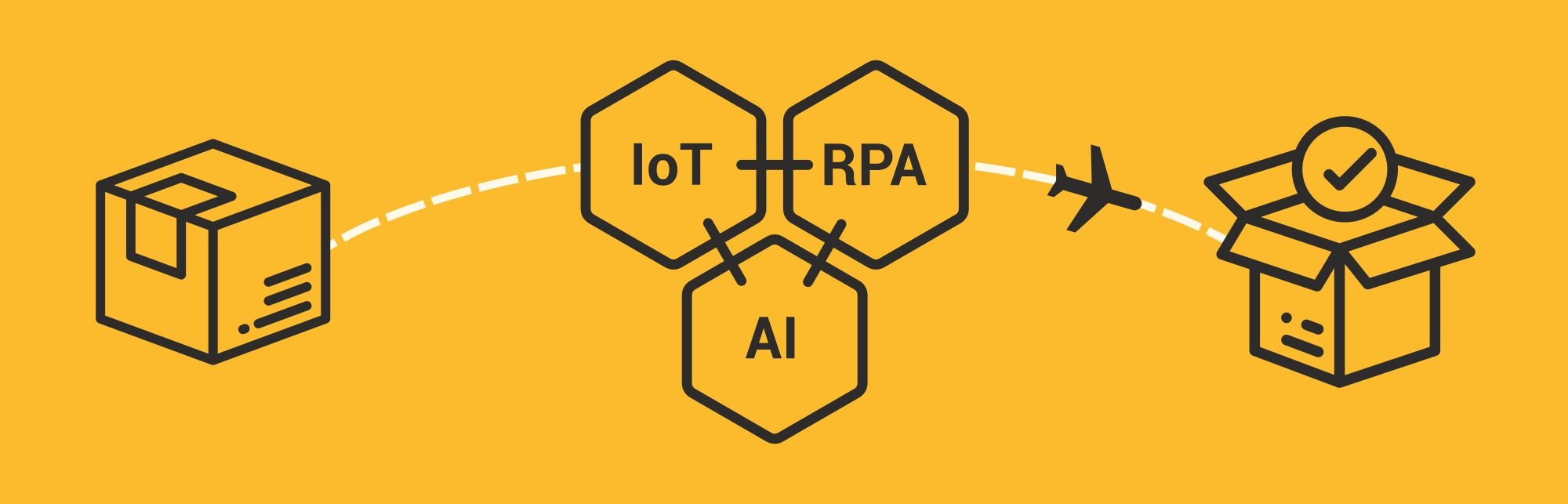
You’ve booked your goods from Zurich to Kansas City. It’s an air shipment that is typically routed through Delta Airlines. The catch here though is that there is a significant time difference in clearance-upon-arrival depending on whether the shipment flies on a cargo plane (quicker clearance) or a passenger plane (takes longer to screen upon arrival) which departs just 5 minutes later. These planes land at different bays at Hartsfield International Airport in Atlanta, which means the time that your goods take to clear customs will vary by several hours.
In other words, this small 5 minute difference in departure can snowball into hours of delay along the way.
The IoT sensors placed with your goods come in handy to identify where and when the flight took off. The RPA algorithm can log in to Delta’s cargo system and confirm the flight on which the parcel was booked by matching consignment ID with flight ID, because it is impractical to use APIs to integrate with every flight cargo portal you are using. IoT + RPA together can then accurately identify which flight your consignment is on.
Now based on this info, the AI bot predicts when the consignment would be cleared, the most cost-effective option to haul the goods from Atlanta to Kansas, and further on. The RPA kicks in once again to log into the delivery vendor’s consignment booking portal and assign the pickup request for the cargo to be moved from Atlanta airport to Kansas upon clearance.
Now, if there is a delay at any if these steps, IoT once again identifies the delay, AI makes a decision based on it, and RPA implements it by rescheduling the delivery slot and changing the delivery agent if needed.
All of this with zero human intervention!
In Summary
When it comes to supply chain automation, think of IoT as the eyes and ears, AI as the mind, and RPA the limbs of a supply chain automation system. One without the other puts you in a difficult spot.
There are many examples of IoT + AI working together to make smart, sometimes even prescriptive predictions, but without RPA, the action cannot be automated.
There are also many examples of AI + RPA working together to automate many functions in the enterprise, but without IoT sensor data, AI bots cannot make informed decisions.
You need all three! This sweet combination of IoT + AI + RPA is set to power the digital enterprises of the future, and it’s the recipe that Roambee is pioneering today.
Watch IoT + AI + RPA in action! |